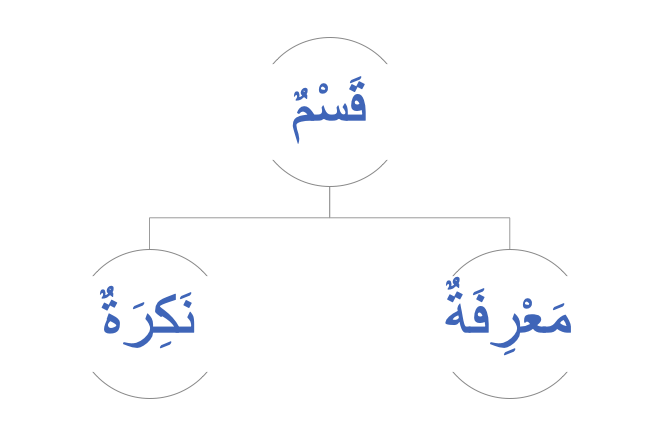
قَسْمٌ

The قَسْمٌ refers to the إِسْمٌ being نَكِرةٌ (Common) or مَعْرِفَةٌ (proper). In English these are called indefinite and definite respectively.
نَكِرةٌ
نَكِرةٌ is that إِسْمٌ which denotes something unspecified, in English usually accompanied with the indefinite article ‘a/an’. Example:
رَجُلٌ
a man
مَعْرِفَةٌ
مَعْرِفَةٌ is that إِسْمٌ which denotes something specific, in English usually accompanied with definite article ‘the’. Example:
There are seven kinds of مَعْرِفَةٌ:
1. الْمُعَرِّفُ بِاللَّام : It is that إِسْمٌ which has الـ (لام التعريف) at the beginning. , in English usually accompanied with definite article ‘the’. For example:
الرَّجُلُ
The man
Adding الـ (the definite article) makes it definite (مَعْرِفَة).
The تَنْوِيْنٌ (ـٌ) is removed, and the word takes ضَمَّةٌ (ـُ) instead.

You may want to review the lesson ‘Sun and Moon Letters’ as a reminder of the rules of placement of الـ (لام التعريف) at the beginning of an إِسْمٌ.
2. عَلَمٌ : It is a proper إِسْمٌ i.e. name of a specific person, place, thing etc. For example:
مُحَمَّدٌ ، مَكَّةُ ، مُوْسىٰ
3. ضَمَائِرٌ : Pronouns such as هُوَ (he).
هُوَ، هُما ، هُمْ
هِيَ ، هُما ، هُنَّ
أَنْتَ ، أَنْتُما ،أَنْتُمْ
أَنْتِ ، أَنْتُما ، أَنْتُنَّ
أَنا ، نَحْنُ
4. المُنَادَىٰ : The one being called. For example:
!يا وَلَدُ! ، يا مُحَمَّد
5. أَسْمَاءُ الإِشَارَةِ : Pointing أَسْمَاءُ such as هَٰذَا (this).
هَٰذَا، هَٰذَانِ، هَٰؤُلَآءِ
هَٰذِهِ، هَٰتَانِ، هَٰؤُلَآءِ
ذٰلِكَ، ذَانِكَ، أُوْلَٰئِكَ
تِلْكَ، تَانِكَ، أُوْلَٰئِكَ
6. أَسْماءُالإِشَارَةِ : Connector words such as الَّذِي (the one who).
7. If the الْمُضَافُ إِلَيْهِ is نَكِرةٌ then the المُضَافُ is نَكِرةٌ.
The topics outlined above will be covered in greater detail throughout the course.